“ 개 같이 코딩해서 정승처럼 사표쓴다. ”
- 개발자 속담(Programmer’s Proverbs)

ES6 클래스 문법은 좀더 JAVA스럽게 객체 지향적으로 표현하기 위해 추가된 새로운 문법이다.
ES5까지 자바스크립트에는 클래스가 없었다. 그래서 프로토타입 체이닝을 통해 클래스 비스무리하게 구현해왔었는데 ES6 버젼에 들어서면서 클래스와 비슷한 구조 문법을 추가하였다.
다만 생김새만 클래스 구조이지, 엔진 내부적으로는 프로토타입 방식으로 작동된다.
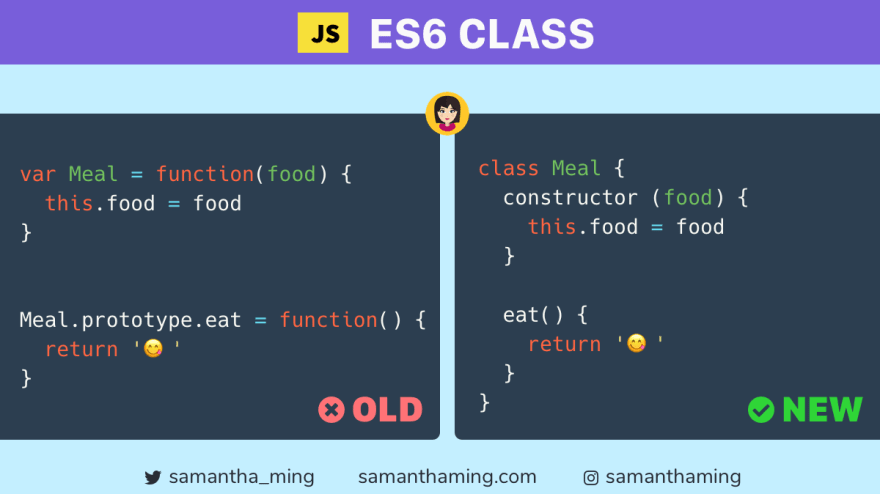
다음은 프로토타입 문법과 클래스 문법의 간단한 차이이다.
이 둘은 같은 결과를 출력하지만, 문법 생김새만 다르고 내부 로직은 완전히 같은 구조라는 점만 기억하면 된다.
ES5 프로토타입 문법
// 생성자
function Person({name, age}) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.introduce = function() {
return `안녕하세요, 제 이름은 ${this.name}입니다.`;
};
const person = new Person({name: '윤아준', age: 19});
console.log(person.introduce()); // 안녕하세요, 제 이름은 윤아준입니다.
ES6 클래스 문법
// 클래스
class Person {
// 이전에서 사용하던 생성자 함수는 클래스 안에 `constructor`라는 이름으로 정의합니다.
constructor({name, age}) { //생성자
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 객체에서 메소드를 정의할 때 사용하던 문법을 그대로 사용하면, 메소드가 자동으로 `Person.prototype`에 저장됩니다.
introduce() {
return `안녕하세요, 제 이름은 ${this.name}입니다.`;
}
}
const person = new Person({name: '윤아준', age: 19});
console.log(person.introduce()); // 안녕하세요, 제 이름은 윤아준입니다.자바스크립트 클래스 문법
Class 선언
constructor는 인스턴스를 생성하고 클래스 필드를 초기화하기 위한 특수한 메서드이다.
constructor는 클래스 안에 한 개만 존재할 수 있다. 2개 이상 있을 경우 Syntax Error가 발생하니까 주의하자.
class Person {
height = 180; // 인스턴스 변수
// constructor는 이름을 바꿀 수 없다.
constructor(name, age) {
// this는 클래스가 생성할 인스턴스를 가리킨다.
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
let person1 = new Person('john', 23);
console.log(person1.name); // john
console.log(person1.age); // 23
console.log(person1.height); // 180클래스 필드의 선언과 초기화는 반드시 constructor 내부에서 실시한다.
constructor 내부에 선언한 클래스 필드는 클래스가 생성할 인스턴스에 바인딩 된다.
클래스 필드는 그 인스턴스의 프로퍼티가 되며, 인스턴스를 통해 클래스 외부에서 언제나 참조할 수 있다. (public)
JAVA나 Python의 클래스문법과의 차이점은, 자바스크립트의 클래스 문법에선 인스턴스 변수를 반드시 지정하지 않고 생성자(constructor)을 통해 this.변수 문법으로 자동 생성될수 있다는 점이다.
클래스의 본문(body)은 strict mode에서 실행된다. 성능 향상을 위해 더 엄격한 문법이 적용된다.
Class 메소드 정의
클래스의 메소드를 정의할 때는 객체 리터럴에서 사용하던 문법과 유사한 문법을 사용한다.
class Calculator {
add(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
subtract(x, y) {
return x - y;
}
}
let calc = new Calculator();
calc.add(1,10); // 11
객체 리터럴의 문법과 마찬가지로, 임의의 표현식을 대괄호로 둘러싸서 메소드의 이름으로 사용할 수도 있다.
const methodName = 'introduce'; // 클래스 메소드 이름
class Person {
constructor({name, age}) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 아래 메소드의 이름은 `introduce`가 됩니다.
[methodName]() {
return `안녕하세요, 제 이름은 ${this.name}입니다.`;
}
}
console.log(new Person({name: '윤아준', age: 19}).introduce()); // 안녕하세요, 제 이름은 윤아준입니다.
Getter / Setter
클래스 내에서 Getter 혹은 setter를 정의하고 싶을 때는 메소드 이름 앞에 get 또는 set을 붙여주면 된다.
[JS] 📚 자바스크립트 Getter & Setter 개념 정리
프로퍼티 getter와 setter 객체의 프로퍼티는 두 종류로 나뉩니다. 첫 번째 종류는 데이터 프로퍼티(data property) 입니다. 지금까지 사용한 모든 프로퍼티는 데이터 프로퍼티입니다. 두 번째는 접근
inpa.tistory.com
class Account {
constructor() {
this._balance = 0;
}
get balance() {
return this._balance;
}
set balance(newBalance) {
this._balance = newBalance;
}
}
const account = new Account();
account.balance = 10000;
account.balance; // 10000
정적 메서드 (static)
정적 메서드는 클래스의 인스턴스가 아닌 클래스 이름으로 곧바로 호출되는 메서드이다.
static 키워드를 메소드 이름 앞에 붙여주면 해당 메소드는 정적 메소드가 된다.
우리가 랜덤값을 얻기 위해 Math.random() 같은 메서드를 쓰듯이, 따로 new Math() 없이 곧바로 클래스명.메서드명 으로 함수를 호출해서 사용하는 것이 바로 radom 메소드가 static으로 설정되어 있기 때문이다.
class Person {
constructor({ name, age }) { // 생성자 인스턴스
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
static static_name = 'STATIC'; // 정적 인스턴스
getName() { // 인스턴스(프로토타입) 메소드
return this.name;
}
static static_getName() { // 정적 메소드
return this.static_name;
}
}
const person = new Person({ name: 'jeff', age: 20 });
person.getName(); // jeff
Person.static_getName(); // STATICclass Person {
constructor({ name, age }) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 이 메소드는 정적 메소드
static static_sumAge(...people) {
/*
함수 파라미터 people를 전개연산자 ...people를 통해 배열로 만듬
[ {"name": "윤아준", age": 19}, { "name": "신하경","age": 20 }]
*/
// 그리고 각 객체의 age값을 얻어와 합침
return people.reduce((acc, person) => acc + person.age, 0);
}
}
const person1 = new Person({ name: '윤아준', age: 19 });
const person2 = new Person({ name: '신하경', age: 20 });
Person.static_sumAge(person1, person2); // 39
제너레이터
Generator 메소드를 정의하려면, 메소드 이름 앞에 * 기호를 붙여주면 된다.
[JS] 📚 제너레이터 - 이터레이터 강화판
제네레이터란? 이터러블이며 동시에 이터레이터 = 이터레이터를 리턴하는 함수 (async가 Promise를 리턴하는 함수듯이, 제너레이터는 이터레이터를 리턴하는 함수다.) 제너레이터 함수를 사용하
inpa.tistory.com
class Gen {
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
}
}
// 1, 2, 3이 차례대로 출력됩니다.
for (let n of new Gen()) {
console.log(n);
}클래스 상속 (Class Inheritance)
클래스 상속(class inheritance, subclassing) 기능을 통해 한 클래스의 기능을 다른 클래스에서 재사용할 수 있다.
extends 키워드
extends 키워드는 클래스를 다른 클래스의 하위 클래스로 만들기 위해 사용된다.
class Parent {
// ...
}
class Child extends Parent {
// ...
}위 코드에서, extends 키워드를 통해 Child 클래스가 Parent 클래스를 상속했다.
이 관계를 보고 '부모 클래스-자식 클래스 관계' 혹은 '슈퍼 클래스(superclass)-서브 클래스(subclass) 관계'라고 말하기도 한다.
따라서 어떤 클래스 A가 다른 클래스 B를 상속받으면, 다음과 같은 일들이 가능해진다.
- 자식 클래스 A를 통해 부모 클래스 B의 정적 메소드와 정적 속성을 사용할 수 있다.
- 부모 클래스 B의 인스턴스 메소드와 인스턴스 속성을 자식 클래스 A의 인스턴스에서 사용할 수 있다.
class Parent {
static staticProp = 'staticProp';
static staticMethod() {
return 'I\'m a static method.';
}
instanceProp = 'instanceProp';
instanceMethod() {
return 'I\'m a instance method.';
}
}
class Child extends Parent {}
// 상속하면 부모의 static요소들을 사용 가능
console.log(Child.staticProp); // staticProp
console.log(Child.staticMethod()); // I'm a static method.
// 상속하면 부모의 인스턴스를 사용 가능
const c = new Child();
console.log(c.instanceProp); // instanceProp
console.log(c.instanceMethod()); // I'm a instance method.
super 키워드
super 키워드의 동작 방식은 다음과 같다.
- 생성자 내부에서 super를 함수처럼 호출하면, 부모 클래스의 생성자가 호출
- 정적 메소드 내부에서는 super.prop과 같이 써서 부모 클래스의 prop 정적 속성에 접근할 수 있다.
- 인스턴스 메소드 내부에서는 super.prop과 같이 써서 부모 클래스의 prop 인스턴스 속성에 접근할 수 있다.
super(); // 부모 생성자
super.메소드명 // 접근class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
sum(){
return (this.first + this.second);
}
}
class Person2 extends Person{
// override Person
constructor(name, first, second, third){
super(name, first, second); //부모 생성자를 가져와서 행하게 한다.
this.third = third;
}
sum(){
// 부모 메소드를 가져와서 사용.
// 오버로딩 메소드에서 온전한 부모 메소드를 사용하고 싶을때
return super.sum() + this.third;
}
}
var kim = new Person2('kim', 10, 20, 30);
document.write(kim.sum()); // 60Private 클래스 변수
이전까지 자바스크립트 클래스의 모든 메서드는 퍼블릭으로 지정되었다.
그래서 유명무실한 반쪽짜리 클래스 구현체로 비난을 받아왔지만, ES2021부터는 메서드와 필드명 앞에 "#"을 붙여서 프라이빗 메서드와 필드 정의가 가능해졌다. (보다 JAVA 스러워졌다)
# 기호를 접두사로 사용하여 메서드와 접근자를 비공개로 설정할 수 있으며 동시에 getter 및 setter 메서드를 사용할 수도 있다.
class myClass {
// private 변수
#num = 100
// private 메서드
#privMethod(){
console.log(this.#num); // 프라이빗 변수 호출
}
publicMethod() {
this.#privMethod(); // 프라이빗 메소드 호출
}
}
let newClass = new myClass();
newClass.publicMethod() // 100
Private Fields 체크하기
private 변수를 클래스에 추가하는 것 까지는 좋았지만, 클래스를 이용할때, 이 클래스 인스턴스가 private인지 public인지 확인이 어려운 경우가 있었다.
왜냐하면 public 필드에 대해 클래스의 존재하지 않는 필드에 접근을 시도하면 undefined가 반환되는 반면에, private 필드는 undefined대신 예외를 발생시키게 되기 때문이다. 그래서 특정 객체에 어떤 private 프로퍼티가 있는지 확인하기 어려웠다.
따라서 in 키워드를 사용해 이 객체안에 private 속성/메소드 가 있는지를 체크할 수 있다.
class Foo {
#brand = 100;
static isFoo(obj) {
return #brand in obj;
}
}
const foo = new Foo();
const foo2 = { brand: 100 };
console.log('foo : ', Foo.isFoo(foo)); // true
console.log('foo2 : ', Foo.isFoo(foo2)); // false클래스 상속 & 프로토타입 상속 문법 비교
클래스 상속은 내부적으로 프로토타입 상속 기능을 활용하고 있다.
아래 코드의 클래스 상속에 대한 프로토타입 체인을 그림으로 나타내보면 다음과 같이 된다.
class Person {}
class Student extends Person {}
const student = new Student();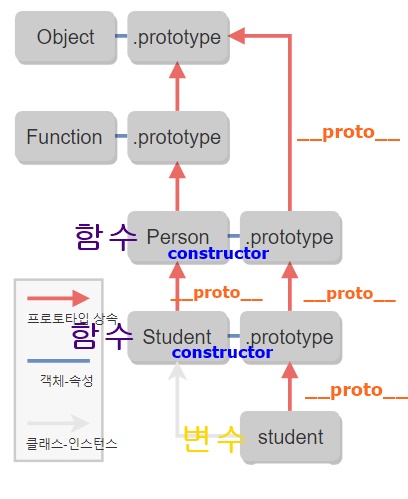
프로토타입 상속 방식
//프로토타입 방식
function Person(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
Person.prototype.sum = function() {
return (this.first + this.second);
}
function Student(name, first, second, third){
Person.call(this, name, first, second);
//Person은 생성자 함수이다. 그냥 쓰면 this는 뭔데? 그래서 이때 call,bind함수를 써준다.
//클래스의 super() 와 같은 역할을 한다고 보면 된다. 하지만 아직 상속이 된건 아니다.
this.third = third;
}
//방법 1 비표준 :
//Student 프로토타입 오브젝트 링크를 Person 프로토타입 오브젝트로 연결시켜 sum을 사용할수있게 찾아가도록 설정
Student.prototype.__proto__ = Person.prototype;
//방법 2 표준 :
//Person프로토타입 오브젝트를 새로 만들어서 대입
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Student.prototype.constructor = Student; //생성자 연결
Student.prototype.avg = function(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
var kim = new Student('kim', 10, 20, 30);
클래스 상속 방식
//클래스 방식
class Person{
constructor(name, first, second){
this.name=name;
this.first=first;
this.second=second;
}
sum(){
return (this.first + this.second);
}
}
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name, first, second, third){
super(name, first, second);
this.third = third;
}
sum(){
return super.sum() + this.third;
}
avg(){
return (this.first+this.second+this.third)/3;
}
}
var kim = new Student('kim', 10, 20, 30);
이 글이 좋으셨다면 구독 & 좋아요
여러분의 구독과 좋아요는
저자에게 큰 힘이 됩니다.


